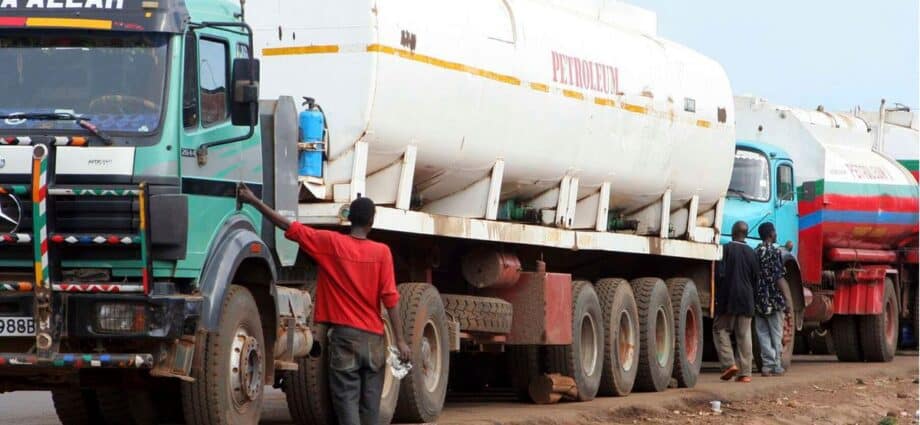
Uganda National Oil Company (Unoc) has started selling petroleum products to oil marketing firms in Tanzania and Uganda as it tests the market ahead of rolling out a direct import deal with Vitol Bahrain.
Officials of oil companies who spoke to this publication say that Unoc has offered products to their subsidiaries in the two countries in small quantities.
Unoc is set to start directly importing from Vitol Bahrain under a five-year deal, as Uganda moves to end decades of relying on Kenyan oil marketing companies (OMCs) for supply of fuel.
Uganda and Kenya fell out after Nairobi inked a government-backed deal to import fuel on credit from three Gulf oil majors. Kampala says middlemen in the deal have led to high pump prices.
“Unoc is currently offering products for sale to OMCs in Tanzania and Uganda. This is fuel supplied by Vitol Group. They (Unoc) have offered the product to our subsidiary companies in Tanzania and Uganda,” an official at one of the OMCs told this publication.
Unoc has over the years been primarily supplying fuel to State-owned entities in Uganda but is now set to start selling to private OMCs.
“They (Unoc) are selling products in what we see as market testing before they scale it up as part of the supply deal with Vitol Bahrain,” an executive of another oil marketer said.
Vitol is a Switzerland-based Dutch oil multinational. It partly owns the Fujairah Refinery in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Uganda kicked off plans for the deal months after Kenya announced an agreement with the Gulf majors to import fuel on a 180-day credit period to ease dollar demand and prop up the shilling.
Kenya started the government-backed deal with Saudi Aramco, Abu Dhabi National Oil Corporation and Emirates National Oil Company in April last year. The deal was set to expire at the end of last year but was extended to December 2024.
Uganda imports an average of 2.5 billion litres of petroleum annually valued at $2 billion (Ksh265 billion), with Kenya Pipeline Company (KPC) handling at least 90 percent of the cargoes.
Besides hitting local OMCs, the Unoc deal with Vitol Bahrain will also significantly hurt KPC’s revenues from transit fuel.
Transit fuel provides at least 40 percent of the dollars that Kenya needs to pay for fuel imports under the government-to-government deal. This is because transit fuel is paid for using dollars.
Unoc had targeted to make the first imports under the deal between January 10-12 this year but missed the target after it failed to get a licence from Kenya.
The licence from the Energy and Petroleum Regulatory Authority (Epra) is key to helping Unoc access the storage and transport network of KPC from the port of Mombasa to Kisumu.
Epra declined to issue the licence on grounds that Unoc has failed to comply with the law. Epra cited Unoc’s failure to show proof of owning a licensed petroleum depot and at least five retail stations in Kenya.