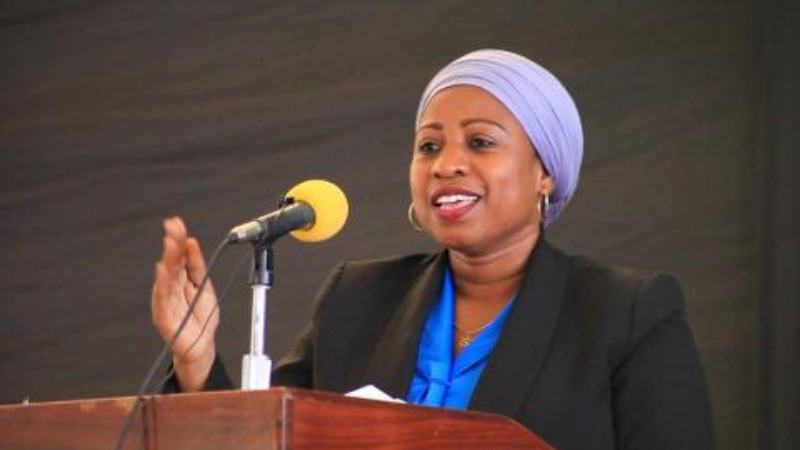
Tanzania’s Minister of Health Hon. Ummy Mwalimu recently disclosed to the media that the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Bill will be read again in Parliament on 31st January 2023, and is expected to come into effect in July of the same year.
The much-awaited universal health coverage means that every Tanzanian citizen, or resident in Tanzania, should have health insurance, whether working or not, which will take care of their health in the country.
Dr. Baghayo Saqware Commissioner of the Tanzania Insurance Regulatory Authority (TIRA), explained that “Once the bill is passed and enacted by Tanzania’s President Samia Suluhu Hassan, it will be enforced after six months of transition to prepare for the implementation.”
The bill was first tabled in parliament in September 2022, after being postponed for several years, and was to be read for a second time on 11th November to be deliberated and passed. However, the parliament decided to return it to the Social Services and Community Development Committee for further consultations.
In addition, Hon. Mwalimu also disclosed that government, through the Ministry Of Health, expects to come up with a guideline for medical expenses in public health service centers in the country, which is expected to come into effect in February 2023.
She made the announcement when she made a surprise visit to the Temeke regional referral hospital to see the state of health care provision as well as listen to the concerns, advice and opinions of the people on the availability of health care services in the country.
Minister Mwalimu said that previously there was no specific guideline for the costs of seeing a doctor, thus causing many centres that provide health services to have different costs that are not compatible, thus causing more inconvenience to the people.
She said that maternity, mother, and child services will continue to be provided free of charge and asked the service providers to comply with the government’s instructions and not to charge the public for these services.
Share this news
This Year’s Most Read News Stories
Serikali: Sampuli zilizochukuliwa hazijathibisha virusi vya Marburg
Wakati Shirika la Afya Duniani (WHO) likisema watu wanane wamefariki dunia kutokana na ugonjwa unaoshukiwa kuwa wa virusi vya Marburg (MVD) mkoani Kagera, Wizara ya Afya ya Tanzania imesema sampuli zilizochukuliwa hazijathibitisha uwepo wa virusi hivyo.Continue Reading

Zanzibar liquor importers face fresh hurdle despite court order
The liquor shortage in Zanzibar is far from over, even after a court order granted relief to the three importers.Continue Reading

Britam half-year net profit hits Sh2bn on higher investment income
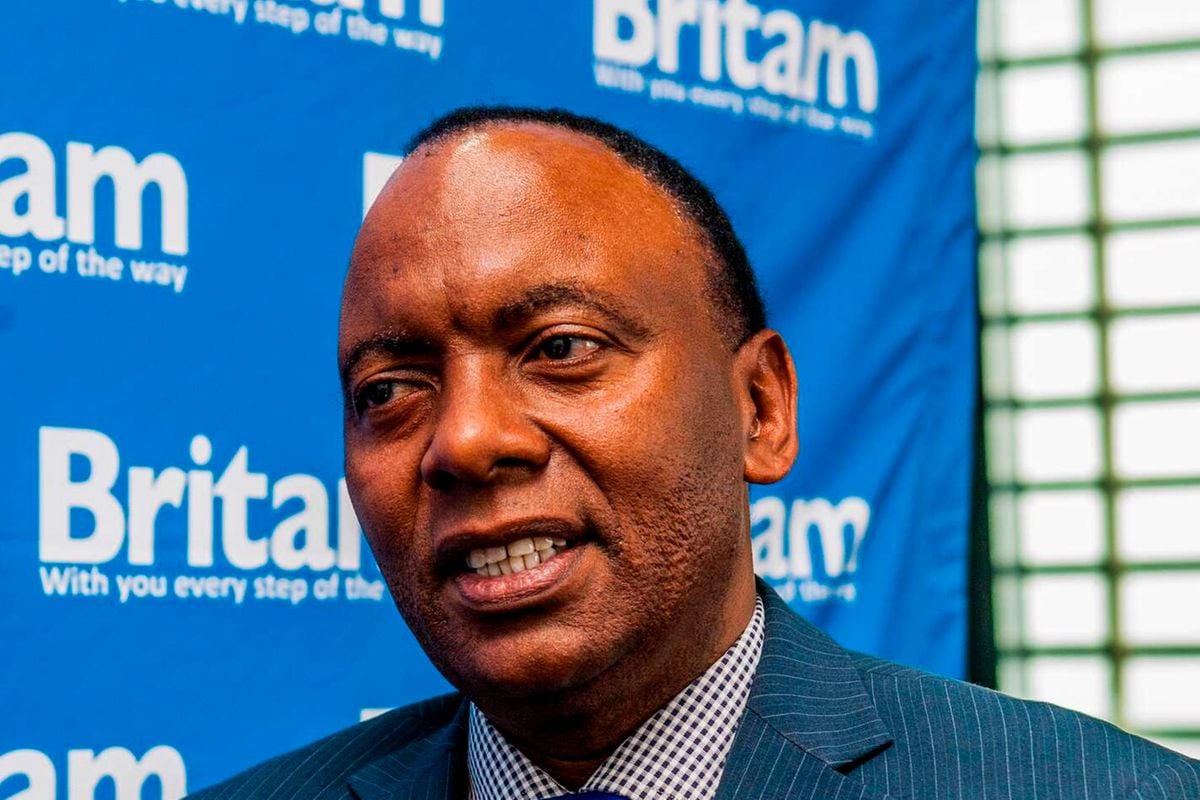

Insurer and financial services provider Britam posted a 22.5 percent jump in net earnings for the half-year ended June 2024, to Sh2 billion, buoyed by increased investment income.
The rise in half-year net profit from Sh1.64 billion posted in a similar period last year came on the back of net investment income rising 2.5 times to Sh13.27 billion from Sh5.3 billion.
“We are confident in the growth and performance trend that Britam has achieved, supported by its subsidiaries in Kenya and the region. Our business is expanding its revenue base while effectively managing costs,” Britam Chief Executive Officer Tom Gitogo said.
“Our customer-centric approach is fueling growth in our customer base and product uptake, particularly through micro-insurance, partnerships, and digital channels.”
The investment income growth was fueled by interest and dividend income rising 34 percent to Sh9.1 billion, which the insurer attributed to growth in revenue and the gains from the realignment of the group’s investment portfolio.
Britam also booked a Sh3.79 billion gain on financial assets at a fair value, compared with a Sh1.8 billion loss posted in a similar period last year.
The increased investment income helped offset the 12.7 percent decline in net insurance service result to Sh2.13 billion in the wake of claims paid out rising at a faster pace than that of premiums received.
Britam said insurance revenue, which is money from written premiums, increased to Sh17.8 billion from Sh16.6 billion, primarily driven by growth in the Kenya insurance business and regional general insurance businesses, which contributed 30 percent of the revenue.
The group has a presence in seven countries in Africa namely Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, South Sudan, Mozambique, and Malawi.
Britam’s insurance service expense hit Sh13.6 billion from Sh11.3 billion, while net insurance finance expenses rose 2.6 times to Sh12.3 billion during the same period.
“Net insurance finance expenses increased mainly due to growth in interest cost for the deposit administration business driven by better investment performance. This has also been impacted by a decline in the yield curve, which has led to an increase in the insurance contract liabilities. The increase has been offset by a matching increase in fair value gain on assets,” said Britam.
Britam’s growth in profit is in line with that of other Nairobi Securities Exchange-listed insurers, which have seen a rise in profits.
Jubilee Holdings net profit in the six months increased by 22.7 percent to Sh2.5 billion on increased income from insurance, helping the insurer maintain Sh2 per share interim dividend.
CIC Insurance Group posted a 0.64 percent rise in net profit to Sh709.99 million in the same period as net earnings of Liberty Kenya nearly tripled to Sh632 million from Sh213 million, while Sanlam Kenya emerged from a loss to post a Sh282.2 million net profit.











